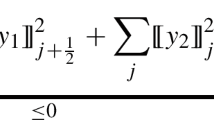Local Linearization-Runge Kutta (LLRK) Methods for Solving Ordinary Differential Equations
- Conference paper
- pp 132–139
- Cite this conference paper

Part of the book series: Lecture Notes in Computer Science ((LNTCS,volume 3991))
Included in the following conference series:
-
1803 Accesses
-
12 Citations
Abstract
A new class of stable methods for solving ordinary differential equations (ODEs) is introduced. This is based on combining the Local Linearization (LL) integrator with other extant discretization methods. For this, an auxiliary ODE is solved to determine a correction term that is added to the LL approximation. In particular, combining the LL method with (explicit) Runge Kutta integrators yields what we call LLRK methods. This permits to improve the order of convergence of the LL method without loss of its stability properties. The performance of the proposed integrators is illustrated through computer simulations.
Chapter PDF
Similar content being viewed by others

Optimized High Order Explicit Runge-Kutta-Nyström Schemes

Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, books and news in related subjects, suggested using machine learning.References
Ascher, U.M., Ruuth, S.J., Spiteri, R.J.: Implicit-Explicit Runge-Kutta methods for time-depending partial differential equations. Appl. Numer. Math. 25, 151–167 (1995)
Beyn, W.J.: On the numerical approximation of phase portraits near stationary points. SIAM J.Numer. Anal. 24, 1095–1113 (1987)
Biscay, R.J., De la Cruz, H., Carbonell, F., Ozaki, T., Jimenez, J.C.: A Higher Order Local Linearization Method for Solving Ordinary Differential Equations. Technical Report, Instituto de Cibernetica, Matematica y Fisica, La Habana (2005)
Bower, J.M., Beeman, D.: The book of GENESIS: exploring realistic neural models with the general neural simulation system. Springer, Heidelberg (1995)
Butcher, J.C.: The Numerical Analysis of Ordinary Differential Equations. Runge-Kutta and General Linear Methods Chichester. John Wiley & Sons, Chichester (1987)
Carroll, J.: A matricial exponentially fitted scheme for the numerical solution of stiff initial-value problems. Computers Math. Applic. 26, 57–64 (1993)
Hairer, E., Wanner, G.: Solving Ordinary Differential Equations II. Stiff and Differential-Algebraic Problems, 3rd edn. Springer, Berlin (1996)
Higham, N.J.: The scaling and squaring method for the matrix exponential revisited. Numerical Analysis Report 452, Manchester Centre for Computational Mathematics (2004)
Hochbruck, M., Lubich, C., Selhofer, H.: Exponential integrators for large systems of differential equations. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 19, 1552–1574 (1998)
Jimenez, J.C.: A Simple Algebraic Expression to Evaluate the Local Linearization Schemes for Stochastic Differential Equations. Appl. Math. Lett. 15, 775–780 (2002)
Jimenez, J.C., Biscay, R.J., Mora, C.M., Rodriguez, L.M.: Dynamic properties of the Local Linearization method for initial-valued problems. Appl. Math. Comput. 126, 63–81 (2002)
Jimenez, J.C., Carbonell, F.: Rate of convergence of local linearization schemes for initial-value problems. Appl. Math. Comput. 171, 1282–1295 (2005)
McLachlan, R.I., Quispel, G.R.W.: Splitting methods. Acta Numer 11, 341–434 (2002)
Moler, C., Van Loan, C.F.: Nineteen dubious ways to compute the exponential of a matrix, twenty-five years later. SIAM Review 45, 3–49 (2003)
Ozaki, T.: A bridge between nonlinear time series models and nonlinear stochastic dynamical systems: a local linearization approach. Statist. Sinica. 2, 113–135 (1992)
Ramos, J.I., Garcia-Lopez, C.M.: Piecewise-linearized methods for initial-value problems. Appl. Math. Comput. 82(1992), 273–302 (1997)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Universidad de Granma, Bayamo, MN, Cuba
H. De la Cruz
Universidad de las Ciencias Informáticas, La Habana, Cuba
H. De la Cruz
Instituto de Cibernética, Matemática y Física, La Habana, Cuba
R. J. Biscay, F. Carbonell & J. C. Jimenez
Institute of Statistical Mathematics, Tokyo, Japan
T. Ozaki
- H. De la Cruz
Search author on:PubMed Google Scholar
- R. J. Biscay
Search author on:PubMed Google Scholar
- F. Carbonell
Search author on:PubMed Google Scholar
- J. C. Jimenez
Search author on:PubMed Google Scholar
- T. Ozaki
Search author on:PubMed Google Scholar
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Advanced Computing and Emerging Technologies Centre, The School of Systems Engineering, University of Reading, RG6 6AY, Reading, United Kingdom
Vassil N. Alexandrov
Department of Mathematics and Computer Science, University of Amsterdam, Kruislaan 403, 1098, Amsterdam, SJ, The Netherlands
Geert Dick van Albada
Faculty of Sciences, Section of Computational Science, University of Amsterdam, Kruislaan 403, 1098, Amsterdam, SJ, The Netherlands
Peter M. A. Sloot
Computer Science Department, University of Tennessee, 37996-3450, Knoxville, TN, USA
Jack Dongarra
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2006 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
De la Cruz, H., Biscay, R.J., Carbonell, F., Jimenez, J.C., Ozaki, T. (2006). Local Linearization-Runge Kutta (LLRK) Methods for Solving Ordinary Differential Equations. In: Alexandrov, V.N., van Albada, G.D., Sloot, P.M.A., Dongarra, J. (eds) Computational Science – ICCS 2006. ICCS 2006. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 3991. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/11758501_22
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/11758501_22
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-540-34379-0
Online ISBN: 978-3-540-34380-6
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)Springer Nature Proceedings Computer Science
Share this paper
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
Keywords
- Phase Portrait
- Local Linearization
- Matrix Exponential
- General Linear Method
- Local Linearization Approximation
These keywords were added by machine and not by the authors. This process is experimental and the keywords may be updated as the learning algorithm improves.